About Your Doctor
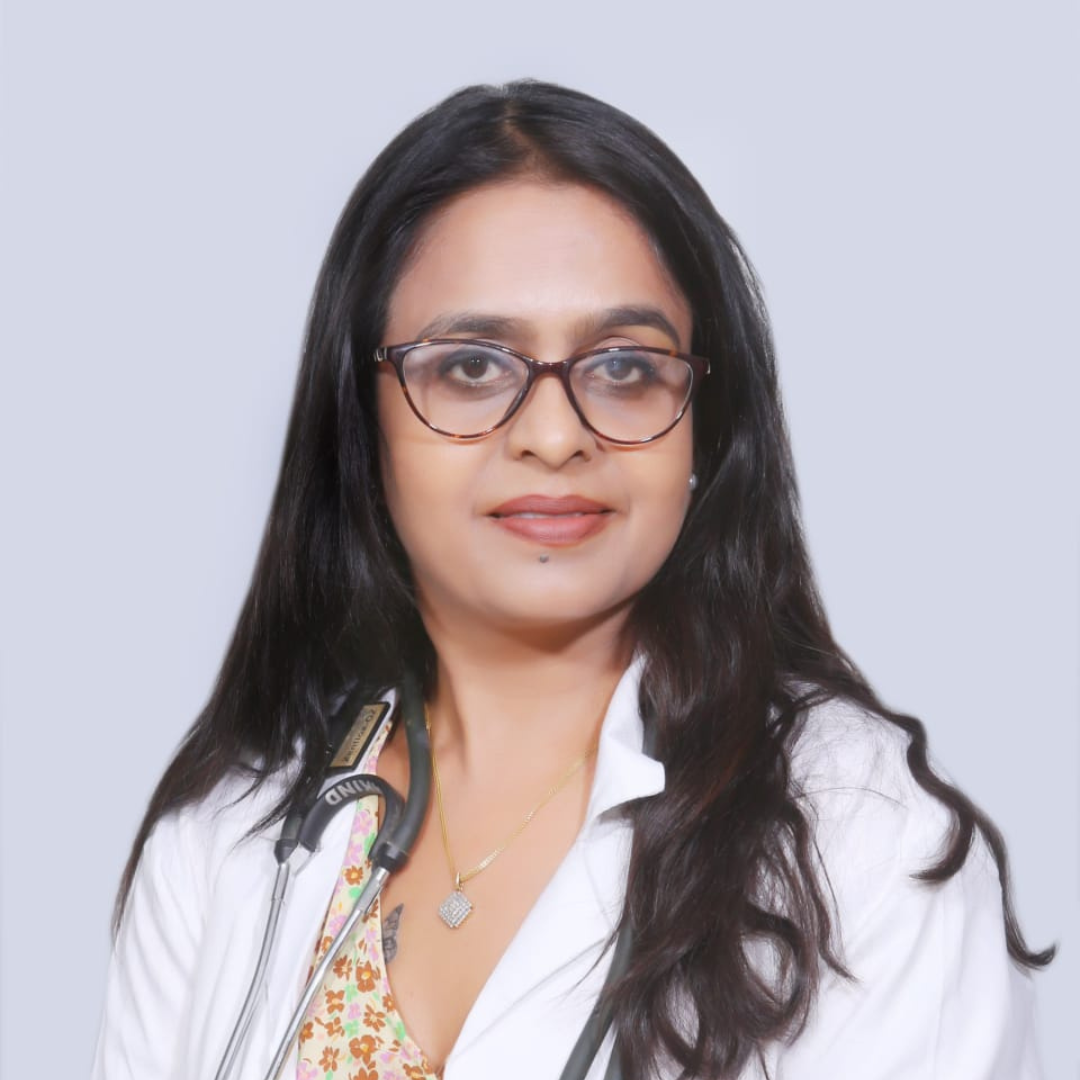
Meet Dr. Ruchi Mishra
Dr. Ruchi Mishra is a highly experienced gynecologist based in Delhi. With over 15 years of dedicated practice in the field of gynecology, she has established herself as a well-known and respected professional. Located in the Delhi University area, Dr. Ruchi Mishra has successfully treated over 10,000 patients, specializing in various areas including pregnancy problems, pelvic infections, multiload insertion, D&C, abortions, and cysts in the uterus. Her expertise also extends to infertility treatments, having helped more than 5,000 patients with medicine-based solutions.